MANUFACTURING
4 links: Forging link , Heat treatment, Grinding processing, Assembly.
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
JB Bearings certifications :
ISO 9001 : 2015,
IATF 16949 : 2016,
EN ISO 12100 : 2010
We also owns certificate utility model patent certificate about
1.Agricultural machine roller grinding device
2.Bearing raceway super-finisher
3.Bearing inner ring rotation mechanism
4.Bearing flaw detection device
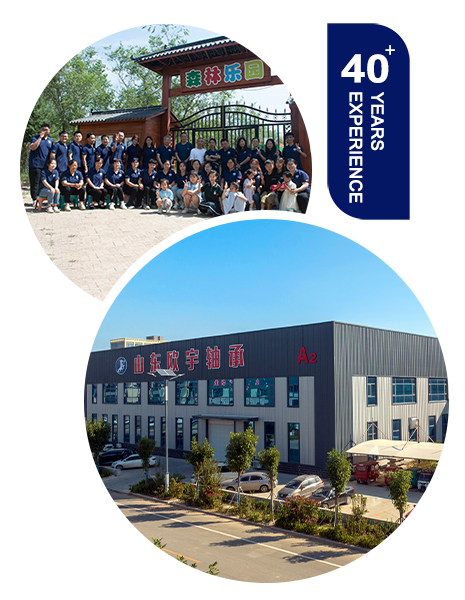

JB BEARINGS CO.,LTD.
With more than 40 years of deep cultivation in the agricultural and industrial fields, JB Bearings has grown into a leading high-end bearing supplier of agricultural and industrial equipment in China.Our products cover the global agricultural machinery industry, with more than 3,000 models and products in 52 countries and regions, and provide services for more than 500 OEM agricultural machinery and industrial equipment manufacturers around the world.

2900
Models & Products

0
Production Lines

0
Countries
400
OEM
OUR APPLICATIONS
Our products cover the global agricultural machinery industry, with more than 3,000 models and products in 52 countries and regions, and provide services for more than 500 OEM agricultural machinery and industrial equipment manufacturers around the world.
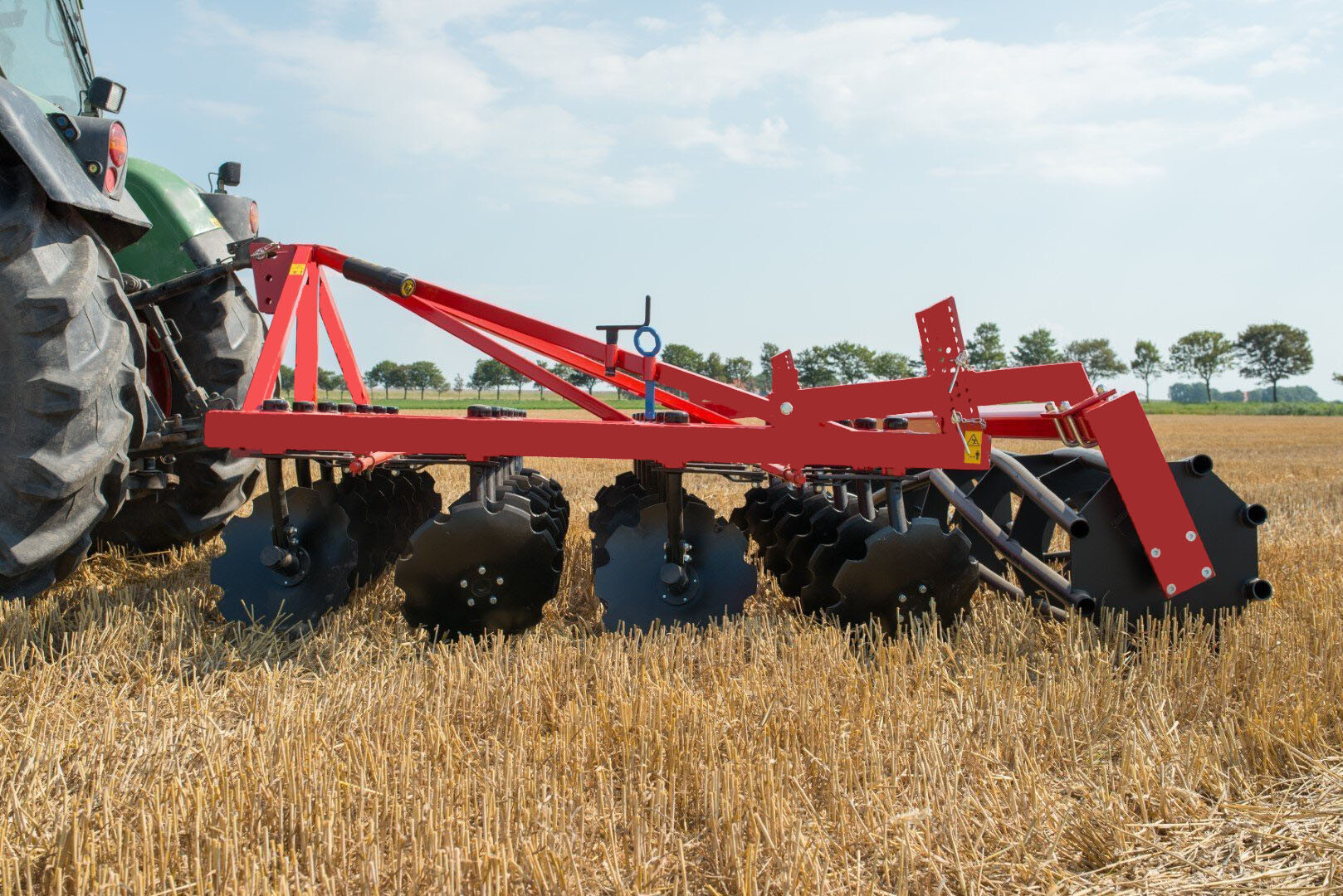

AGRICULTURE
The uptime of farm machinery is critical because unplanned downtime can ruin the planting or harvest season. Whether dirt, debris, extreme temperatures, corrosive chemicals or moisture, agricultural machinery is constantly exposed to a variety of harsh environments. JB agricultural bearings are a reliable choice for farmers.
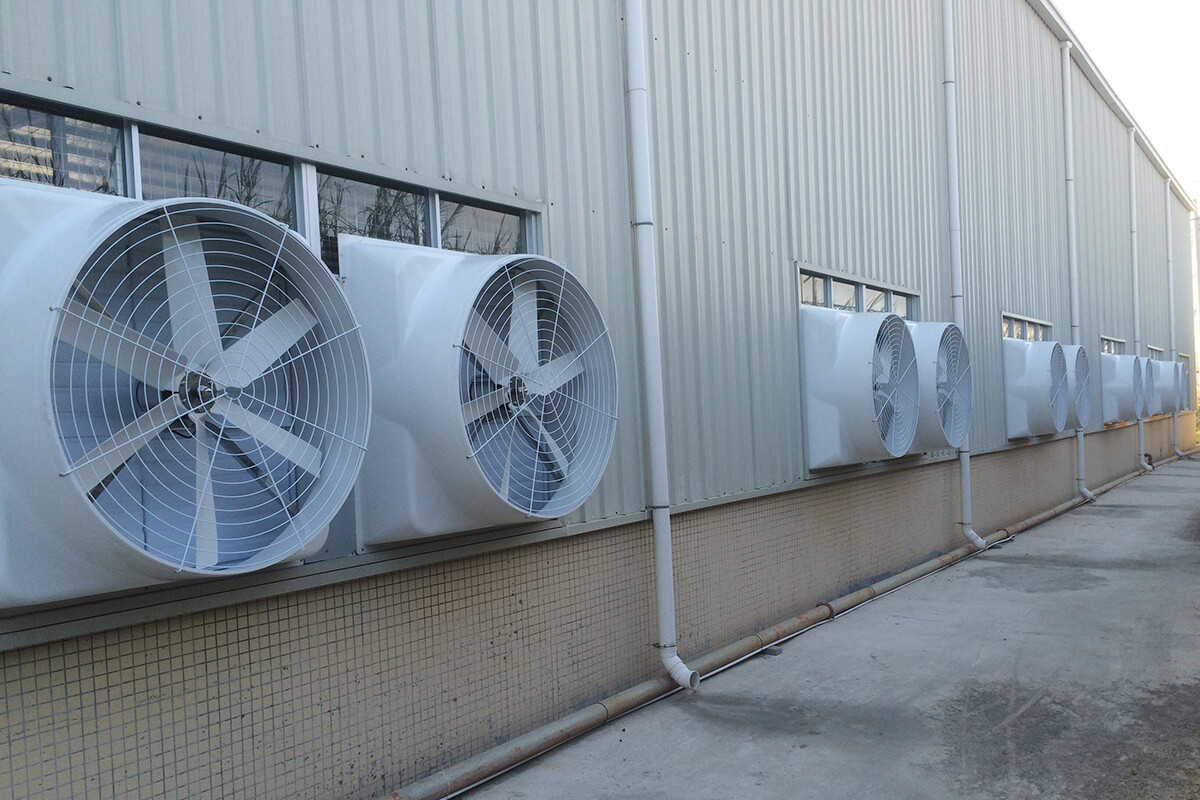

INDUSTRIAL FAN
Bearings in industrial fans operate at high speeds and under relatively light radial loads. These bearings may also operate in extremely hot or cold conditions, or in locations where maintenance is not easy. Fan air is often used to transport materials. Over time, the material will stick to the impeller, causing an imbalance, and even reduce the normal operating time and service life of the fan. JB has developed a range of solutions for industrial fans and HVAC systems. These solutions increase cost effectiveness and enable trouble-free operation.

MATERIAL TRANSFER
Material transfer is an essential component of a business's success in manufacturing, processing, and transporting products to market. To do this effectively, businesses need systems that can maintain performance over time. Production must be kept running, and to ensure this, delivery systems and components need to do the same. Choosing JB Bearings can solve this problem.

NEW ENERGY
With the improvement of global awareness of environmental protection and the awareness of the shortcomings of traditional fuel vehicles, the market demand and development speed of new energy vehicles are growing. As one of the key components of new energy vehicles, bearings play an important role in the performance improvement and reliability assurance of new energy vehicles.
LATEST NEWS
We are willing to work hand in hand with people from all of the files to achieve a win-win situation and create a better life in future.
 2024-07-182024 Agrosalon Exhibition-Booth No. 8-Moscow, RussiaRead More +
2024-07-182024 Agrosalon Exhibition-Booth No. 8-Moscow, RussiaRead More + 2024-07-182024 EIMA Exhibition-Booth No. 35-C8-D6-Bologna, ItalyRead More +
2024-07-182024 EIMA Exhibition-Booth No. 35-C8-D6-Bologna, ItalyRead More + 2024-12-102024 CHINA INTERNATIONAL BEARING INDUSTRY EXHIBITIONRead More +
2024-12-102024 CHINA INTERNATIONAL BEARING INDUSTRY EXHIBITIONRead More + 2024-08-292024 China International Agricultural Machinery ExhibitionRead More +
2024-08-292024 China International Agricultural Machinery ExhibitionRead More +
LEAVE US A MESSAGE
If you have any questions, please fill out the form to contact us, and our customer service will reply to you within 24 hours!
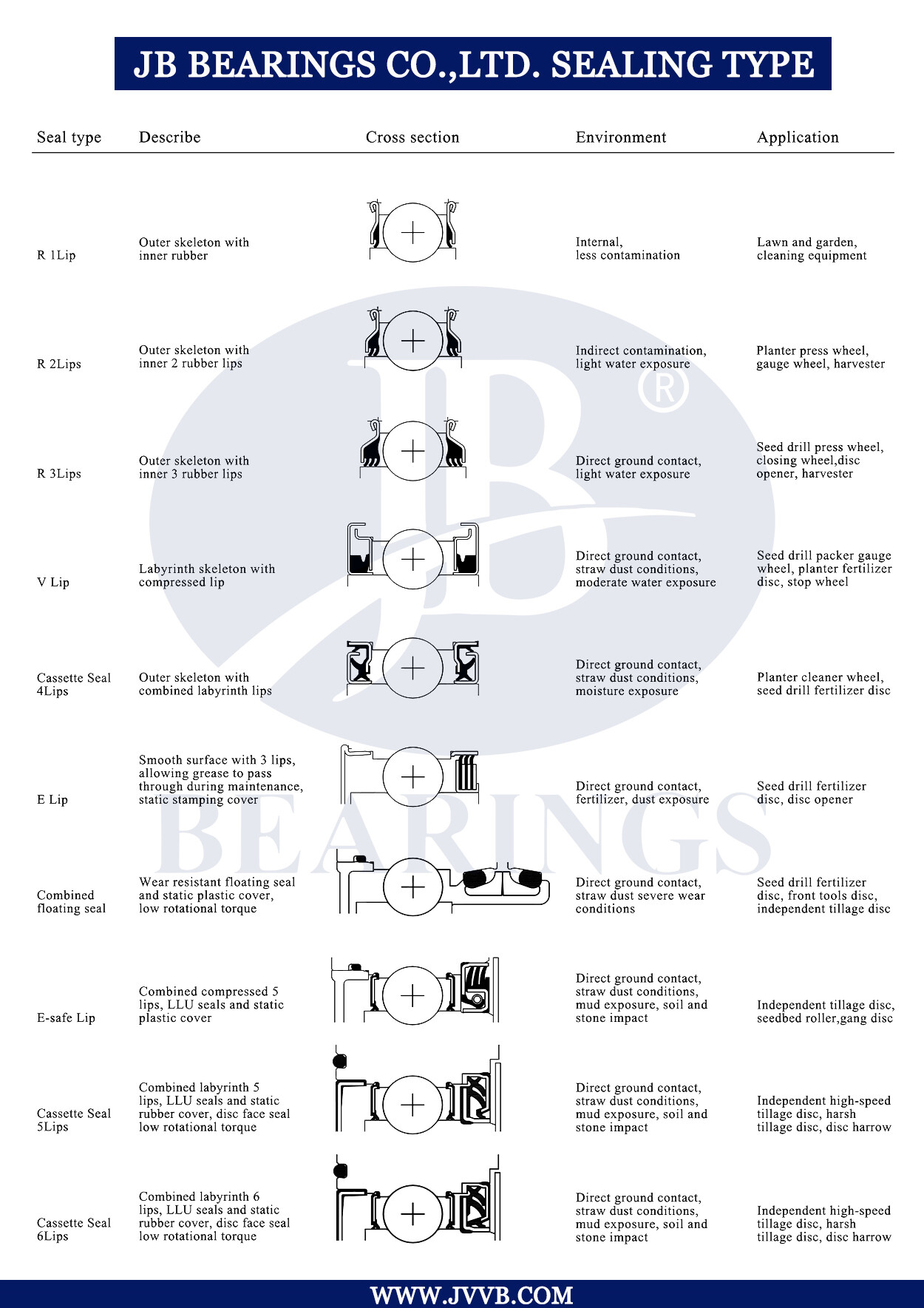
|
Suffixes |
|
|
Sealing Types |
|
|
2Z |
Metal shield (non-contact sealing) on both sides |
|
2RS |
One lip rubber metal seal on both sides |
|
2RS1 |
One lip rubber metal seal on both sides |
|
2S |
One lip rubber metal seal (on both sides) |
|
2F |
One lip rubber metal seal + flinger, on both sides |
|
2T |
Three lip seal on both sides |
|
T |
Outer ring with stopping pin |
|
2TC |
Three lip seal on both sides+ metal cover |
|
2TB |
Three lip seal + metal shield, on both sides |
|
TDT |
Three lip seal at one side, double three lip seal on the other side |
|
FS |
Sealing with one lip seal and a protective metal ring at one side and one lip seal on the other side |
|
TBS |
Sealing with three lip seal and a protective metal ring at one side and one lip seal on the other side |
|
TBT |
Sealing with three lip seal and a protective metal ring at one side and three lip seal on the other side |
|
2P |
Five lip seal on both sides |
|
2PB |
Five lip seal and metal shield, on both sides |
|
2PC |
Five lip seal on both sides + metal cover |
|
P |
Triple lip seal on one side, cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
PP |
Triple lip seal, cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
PB |
Triple lip seal on one side, spherical surface of outer ring |
|
PPB |
Triple lip seal, spherical surface of outer ring |
|
RR |
One lip seal cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
RRB |
One lip seal spherical surface of outer ring |
|
KPP |
Triple lip seal cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
KPPB |
Triple lip seal spherical surface of outer ring |
|
KR |
One lip seal on one side, cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
KRR |
One lip seal, cylindrical surface of outer ring |
|
KRB |
One lip seal on one side, spherical surface |
|
KRRB |
One lip seal, spherical surface |
|
KRP |
One lip seal on one side and on the other side is triple lip seal |


















